Tesla, the trailblazer in electric vehicles (EVs), has been at the forefront of autonomous driving technology for years.
Two key terms that are often used when discussing Tesla’s advanced driver-assistance system (ADAS) are Autosteer and Autopilot.
While these terms are related, they refer to different aspects of Tesla’s autonomous driving features.
In this article, we’ll clarify the relationship between Tesla Autosteer and Autopilot and explore their respective functionalities.
Autosteer primarily focuses on lane keeping and adaptive cruise control, offering partial automation on highways. In contrast, Autopilot is a more comprehensive package that includes Autosteer and extends to features like Full Self-Driving capability, advanced lane-changing, autonomous parking, and potential traffic light/stop sign control, representing a higher level of automation in Tesla’s advanced driver-assistance system (ADAS).
Tesla Autosteer: Precision Lane-Keeping
Autosteer is a vital component of Tesla’s ADAS suite, often referred to as “Enhanced Autopilot.” Its primary focus is on the vehicle’s ability to assist with steering and lanekeeping. Here’s a closer look at the key aspects of Tesla Autosteer:
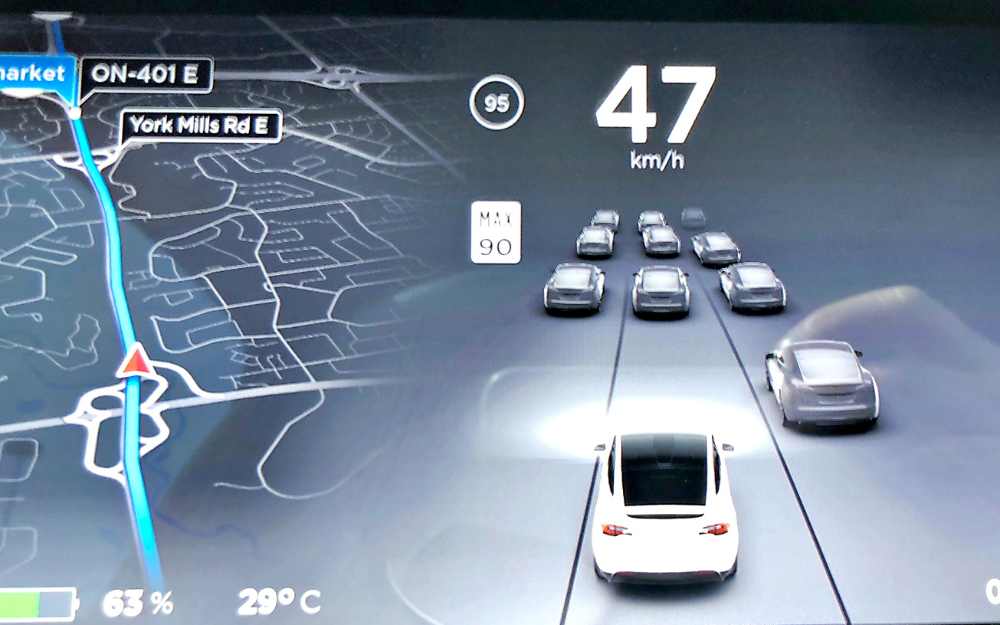
1. Lane Keeping:
Autosteer utilizes a combination of cameras and sensors to detect lane markings on the road.
It actively steers the vehicle to keep it centered within the lane, minimizing the need for continuous manual steering input from the driver.
2. Traffic-Aware Cruise Control:
In addition to lane keeping, Autosteer incorporates Traffic-Aware Cruise Control.
This feature automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed based on the flow of traffic, ensuring it maintains a safe following distance from the vehicle in front.
3. Limited Self-Driving:
Autosteer is categorized as a Level 2 autonomous driving system according to the SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) scale.
It offers partial automation, which means it can control both steering and speed on certain roadways, but it still requires active supervision from the driver.
Drivers are expected to remain engaged and have their hands on the steering wheel at all times.
4. Highway Use:
Tesla recommends using Autosteer primarily on highways and well-marked roads. It is not intended for use on city streets or in complex urban environments.
Tesla Autopilot: A Comprehensive ADAS Package
Tesla Autopilot is a more extensive package that includes Autosteer as one of its core components. Autopilot offers a broader range of capabilities and represents a more advanced stage of autonomous driving technology. Here’s what sets Tesla Autopilot apart:
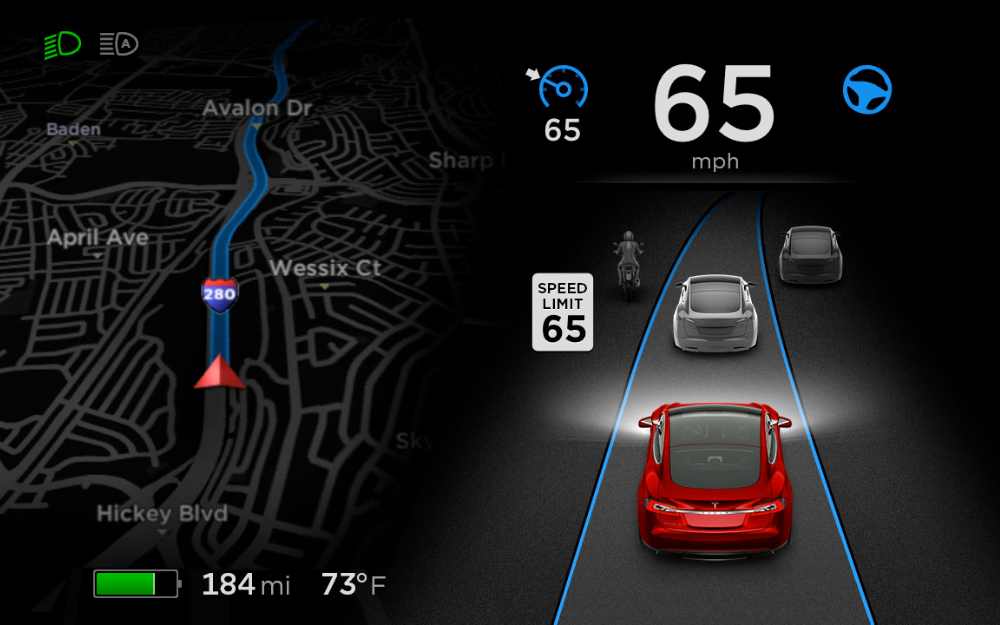
1. Full Self-Driving (FSD) Capability:
Autopilot includes the promise of Full Self-Driving (FSD) capability, which represents a higher level of automation than what Autosteer offers.
FSD aims to enable fully autonomous driving without the need for constant driver intervention.
However, it’s essential to note that the availability and functionality of FSD features may vary by region and are subject to regulatory approval.
2. Navigate on Autopilot:
A standout feature within Tesla Autopilot is “Navigate on Autopilot.” This feature allows the vehicle to automatically change lanes, take highway exits, and navigate complex interchanges while following a GPS route.
It represents a more sophisticated form of autonomous highway driving.
3. Advanced Summon:
Autopilot includes an advanced summon feature, which enables the car to navigate through parking lots autonomously to reach the driver. This feature enhances parking convenience and facilitates easy vehicle retrieval.
4. Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control:
Tesla has been working on features that allow the vehicle to automatically stop at traffic lights and stop signs. While this feature is still in development, it is expected to make life a lot easier on the road.
Conclusion: The Relationship Between Autosteer and Autopilot
Tesla Autosteer and Autopilot are closely related components of Tesla’s ADAS suite.
Autosteer is the foundational feature focused on lane keeping and adaptive cruise control, offering partial automation for highway driving.
Autopilot, on the other hand, is a comprehensive package that includes Autosteer and extends to features like Full Self-Driving capability (under development), Navigate on Autopilot, advanced summon, and potential traffic light/stop sign control.
Understanding this distinction is crucial for Tesla drivers. Regardless of the level of automation, drivers must remain attentive and be prepared to take control of the vehicle at any time, as safety regulations mandate active supervision when using these ADAS features.
As the field of autonomous driving technology continues to evolve, Tesla is likely to introduce updates and enhancements to both Autosteer and Autopilot, pushing the boundaries of human-machine collaboration on the road.
However, until full autonomy is achieved, responsible use of these features in compliance with local regulations remains paramount.

